Forklift assembly line system plant
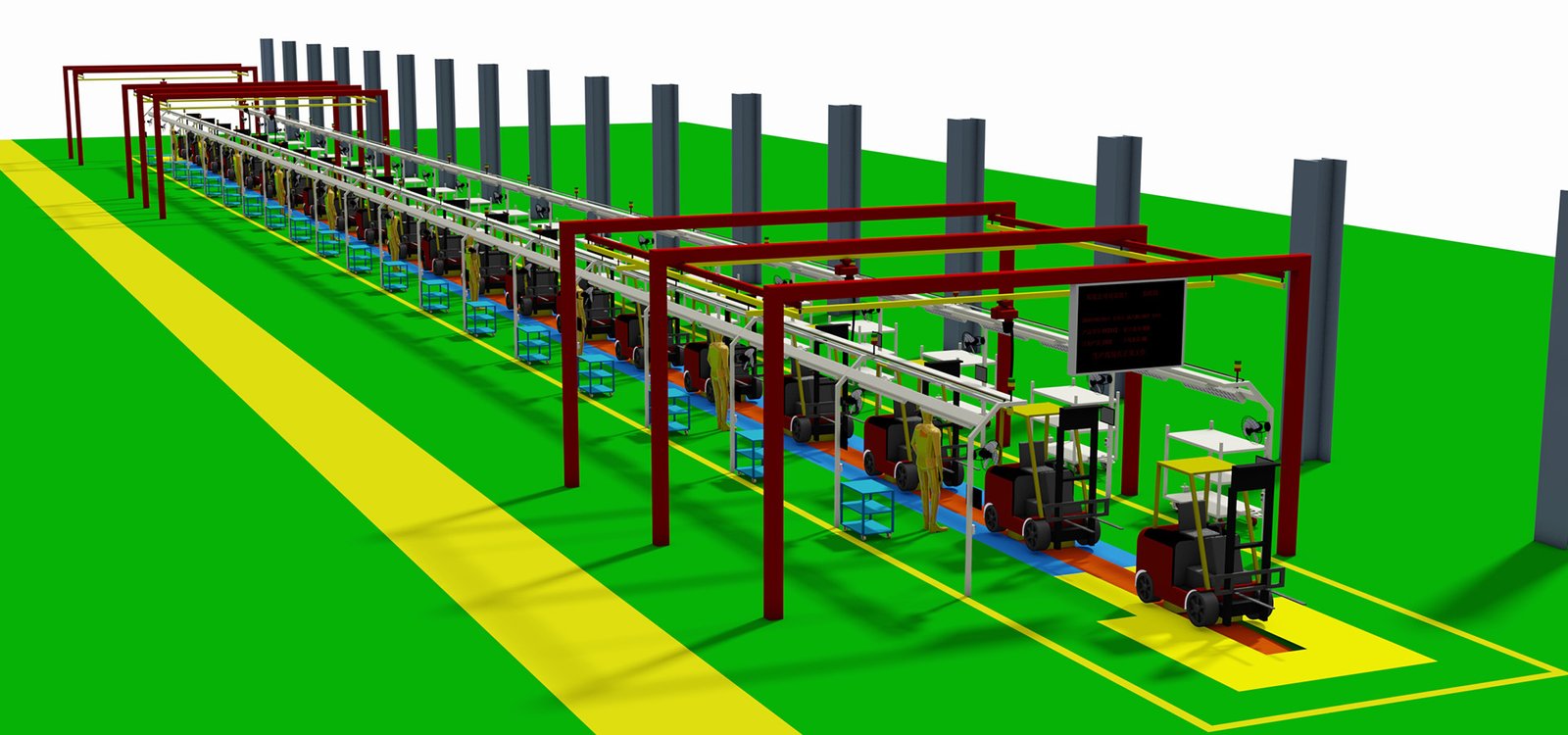
The forklift assembly line production system, incorporating automated workstations, conveyor systems, welding and painting lines, quality inspection stations, MES, material management, electrical and hydraulic assembly, test tracks, service areas, and data analysis, is designed to optimize efficiency, quality, and standardization in forklift manufacturing processes.
The forklift assembly line production system is a complex system that typically consists of the following main components:
- Automated Assembly Lines: Including automated assembly workstations, which may contain robots, automated tools, and equipment for performing forklift assembly tasks.
- Conveyor Systems: Used to transport forklift components from one workstation to another, this may include automated conveyor belts, AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), or other material handling systems.
- Welding and Painting Lines: Metal components of forklifts typically require welding and painting, and these production lines include welding robots, painting equipment, and drying ovens.
- Quality Inspection Stations: Quality inspection stations are set up at various stages of the production line to ensure the assembly quality of parts and the entire vehicle meets standards.
- MES System: The Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a software solution for monitoring and controlling shop floor production processes, including production scheduling, quality control, equipment management, inventory management, and reporting analysis.
- Material Management System: Used for tracking and managing the materials and components required for forklift production, ensuring timely supply and reducing inventory.
- Electrical and Hydraulic System Assembly: Areas specifically for assembling the electrical and hydraulic systems of forklifts.
- Test Tracks: Assembled forklifts need to undergo performance testing on test tracks to verify their operation and safety.
- Service and Maintenance Areas: Used for the final inspection, maintenance, and adjustment of forklifts before delivery.
- Data Collection and Analysis System: Collects production line data for analysis and improvement of the production process.
Forklift manufacturers have adopted advanced automation technologies and MES systems in their production line systems to achieve efficient, standardized production and ensure product quality. For example, Heli has advanced intelligent manufacturing through investments in digital workshops and smart factories, while Hangcha has implemented the intelligent manufacturing direction of automated assembly, welding, painting, and transportation, establishing a smart factory with intelligent robots and intelligent integrated production lines.
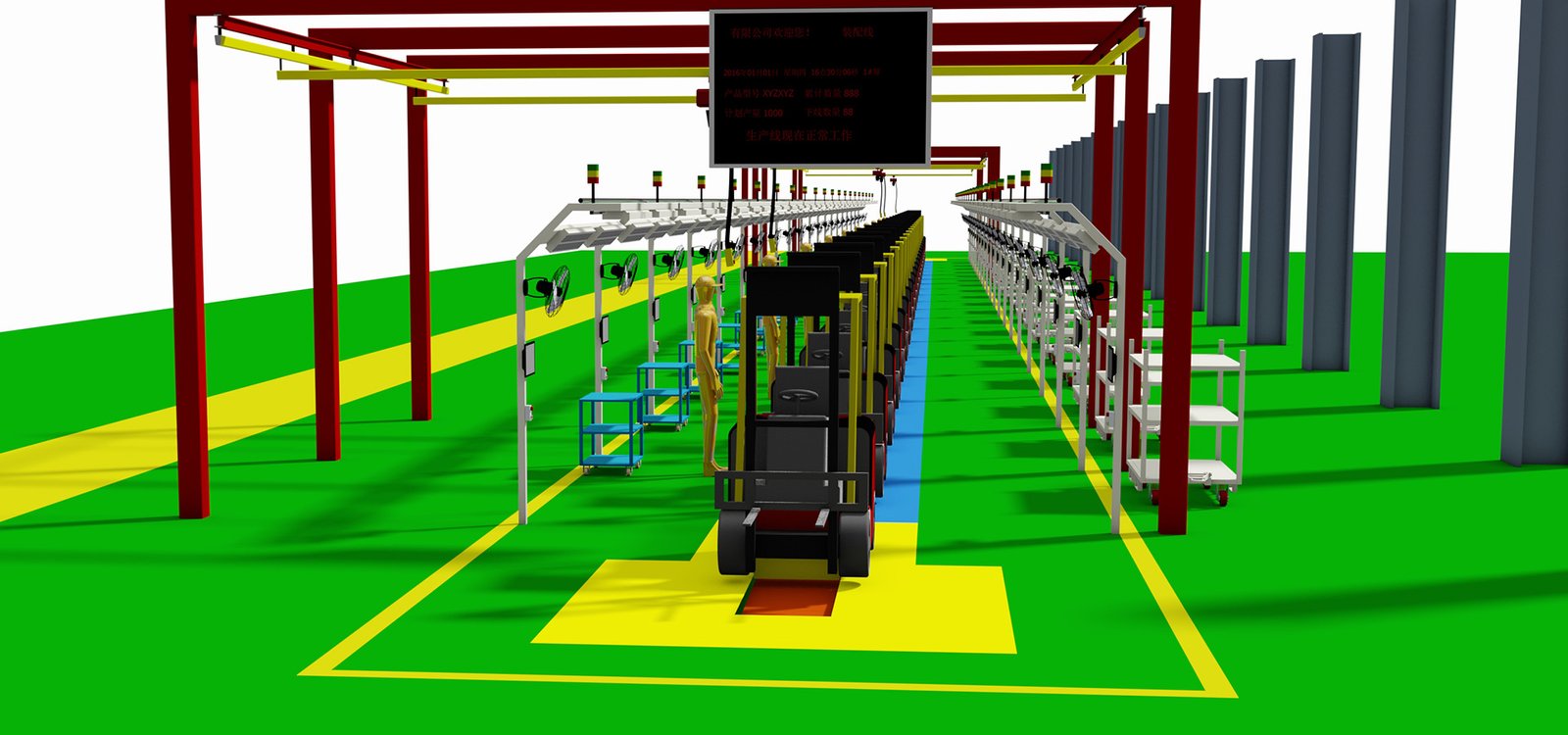
The production output of a forklift production line is closely related to the standardization of the assembly line, and here are some key points outlining their relationship:
- Standardized Processes: Standardized assembly processes ensure that each production step is carried out according to established best practices, thereby improving production efficiency and output.
- Reduced Variability: Standardization reduces variability in the production process, allowing the assembly line to operate consistently, minimizing downtime, and increasing output.
- Ease of Training: Standardized operating procedures make employee training more straightforward and efficient, enabling staff to quickly acquire the necessary skills and reducing the error rate in production.
- Quality Control: Standardization facilitates the implementation of strict quality control measures, ensuring that every forklift coming off the line meets quality standards and reducing rework and scrap rates.
- Material Management: Standardized material management and replenishment processes ensure timely supply of materials on the production line, preventing production delays due to material shortages.
- Equipment Compatibility: Standardized production line equipment and tools simplify maintenance and repair work, reducing production interruptions caused by equipment failures.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Standardized assembly line design allows for easier adjustments and expansions to accommodate changes in market demand and increases in production volume.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Standardization can lead to reduced production costs, as standardized processes are generally more efficient and can minimize waste and improve resource utilization.
- Continuous Improvement: Standardization provides a foundation for continuous improvement, enabling production teams to systematically identify and implement improvement measures, further enhancing output and efficiency.
- Customer Satisfaction: Standardized production helps ensure product consistency and reliability, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and market competitiveness.
In summary, the output of a forklift production line is greatly influenced by the level of standardization of the assembly line. Standardization can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and quality assurance, thereby improving overall output and the company’s market competitiveness.
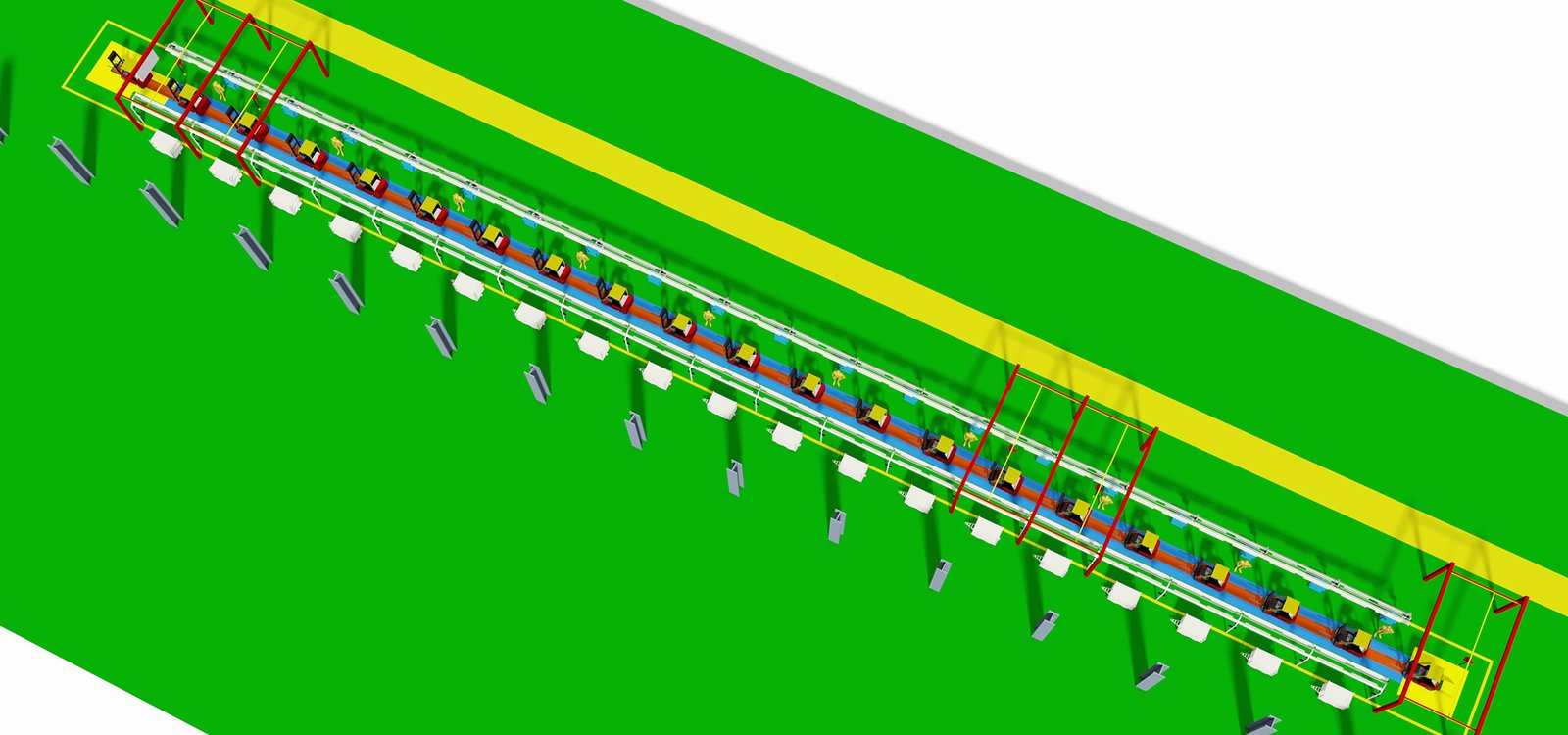
The forklift assembly production process is a series of meticulously designed steps to ensure efficient and high-quality assembly of forklifts from various components to the final product. Here is a typical process for forklift assembly production:
- Design and Planning:
- Forklift design drawings and assembly instructions are prepared.
- Determine the assembly process and required tools and equipment.
- Component Preparation:
- Procure or manufacture various components required, including the engine, chassis, body, forks, hydraulic system components, etc.
- Conduct incoming inspection of components to ensure quality meets standards.
- Chassis Assembly:
- Assemble the forklift’s running gear, including wheels, axles, and suspension systems.
- Install and adjust the braking system.
- Engine Installation:
- Mount the engine onto the forklift chassis and connect the related electrical and fuel systems.
- Hydraulic System Assembly:
- Install the hydraulic pump, cylinders, pipes, and control valves to ensure proper functioning of the lifting and tilting mechanisms.
- Cab and Body Assembly:
- Assemble the forklift’s body structure and cab, including the control panel and seat.
- Electrical System Installation:
- Install batteries, motors, control systems, and lighting equipment.
- For electric forklifts, also install chargers and related electrical protection devices.
- Lifting Mechanism Assembly:
- Install the fork and lifting cylinder to ensure smooth operation of the lifting mechanism.
- System Integration and Testing:
- Connect all systems of the forklift, including hydraulic, electrical, and control systems.
- Conduct functional tests to ensure all components and systems work together.
- Painting:
- Perform surface treatment and painting of the forklift’s metal parts to prevent corrosion and enhance appearance quality.
- Final Inspection and Tuning:
- Carry out a comprehensive inspection, including safety and performance tests.
- Adjust the forklift’s operational performance to meet specified standards.
- Quality Control:
- Conduct the final quality inspection to ensure the forklift meets all shipping requirements.
- Packaging and Shipping:
- Properly package the forklift to protect it from damage during transportation.
- Delivery and After-Sales Service:
- Deliver the forklift to the customer and provide necessary after-sales service and support.
The entire forklift assembly process requires strict quality control and meticulous management to ensure the final product’s high performance and reliability.
