RGV (Rail Guided Vehicle) for assembly lines
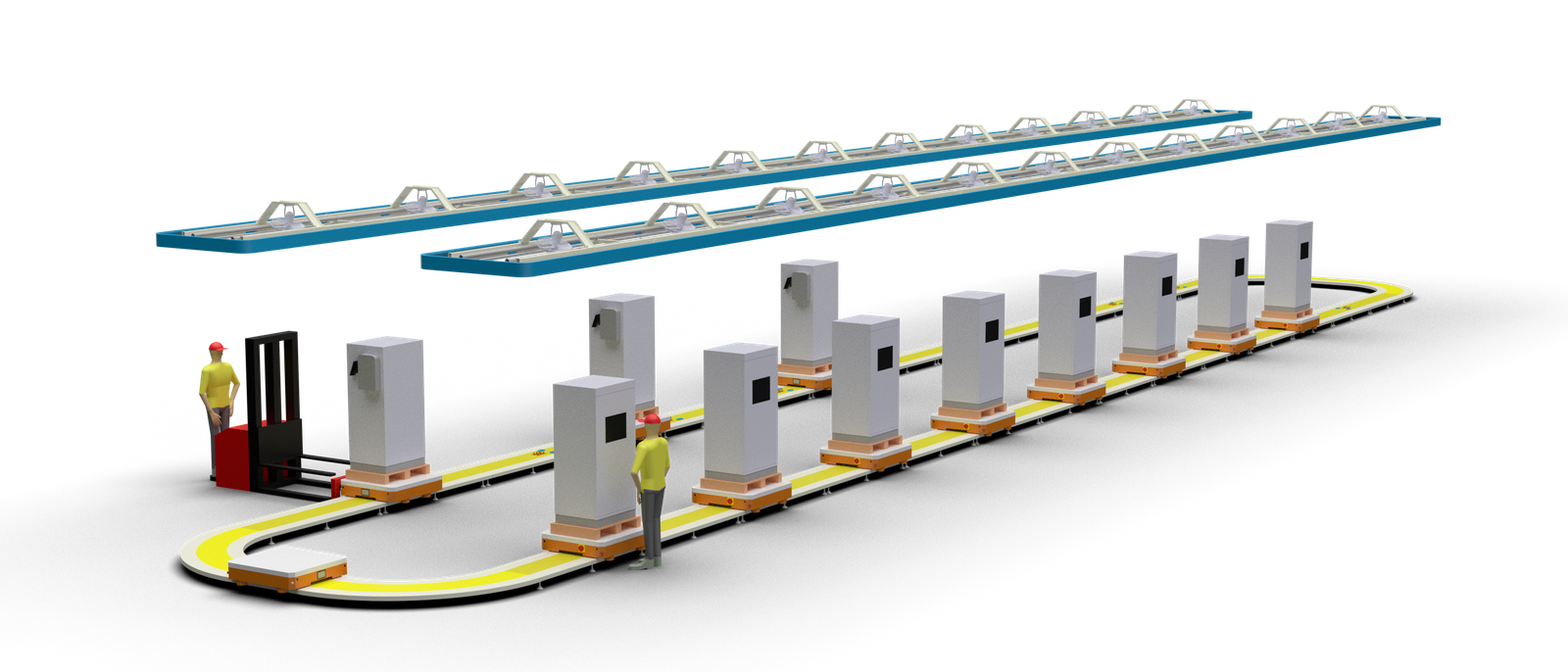
Here is the detailed itemized description of RGV (Rail Guided Vehicle) used in assembly lines:
I. Structural Features
- Vehicle Body Structure
- Composed mainly of the frame, drive wheels, driven wheels, front and rear bumpers, electrical system, and protective cover plates.
- The frame is typically made of high-strength steel, offering excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation.
- Drive System
- Usually employs a combination of servo motors and reducers, supporting bidirectional movement and synchronized control.
- High-end models feature leaf spring suspension structures to ensure the drive wheels remain pressed against the rail, preventing slippage and positioning errors.
- Power Supply
- Commonly uses conductor rail power supply (e.g., brands like VAHLE, Panasonic); some models use battery power.
- Communication and Positioning System
- Communication methods include optical communication, Wi-Fi, RFID, etc.
- Positioning methods include laser ranging, RFID + photoelectric switches, encoder feedback, with positioning accuracy reaching ±2mm to ±5mm.
- Safety Protection System
- Equipped with safety edge switches, laser ranging, optical communication obstruction detection, etc., supporting emergency braking.
II. Control Methods
- Control Modes
- Supports manual, single-machine automatic, and networked automatic modes, allowing flexible switching.
- Scheduling System
- Usually centrally controlled by a host computer, supporting integration with MES systems for task allocation and path optimization.
- Path Control
- Fixed-path operation; rails can be straight, circular, or branched, suitable for multi-station handling.
- Remote Control and Monitoring
- Supports remote control operation, with real-time monitoring, status feedback, and abnormal alarm functions.
III. Advantages
- High Efficiency
- Fast operating speed (up to 160–200 m/min), suitable for high-frequency handling tasks.
- High Reliability
- Fixed rail ensures stable operation, low failure rate, and easy maintenance.
- Precise Positioning
- Combines multiple positioning methods for high repeatability, suitable for high-precision assembly.
- Cost-Effective
- Simple structure, mainly uses standard domestic components, with lower manufacturing and maintenance costs compared to AGVs.
- High Safety
- Reduces manual handling, lowers operational risks; equipped with multiple safety protection mechanisms.
- Strong Adaptability
- Capable of operating in harsh environments (e.g., high temperature, dust), and supports heavy loads (up to 5 tons).
IV. Application Scenarios
- Assembly Lines
- Used in automotive, injection molding, aerospace, and other industries for precise material transport between workstations.
- Automated Warehouses
- Works with automated storage systems to realize automatic material handling, storage, and sorting.
- Production Line Logistics
- Connects with conveyors, lifts, robots, etc., to build automated logistics systems.
- Multi-Variety, Small-Batch Production
- Supports mixed-model production and customized order processing, meeting flexible manufacturing needs.
- Special Environment Applications
- Suitable for cold-rolled steel pipe workshops, chemical plants, aerospace, and other scenarios requiring high handling precision and stability.
