E-bike Production Line ,Electrical Assembly
E-bike Production Line | Electric Bike Assembly Line Solutions
I. Overview
The electric bicycle (e-bike) / electric motorcycle production line is a modern manufacturing system integrating mechanical processing, coating technology, electrical assembly, and intelligent inspection.
Modern e-bike production lines not only meet the demands for large-scale standardized production but also achieve full-process digital management through the MES (Manufacturing Execution System), ensuring product quality consistency and traceability.
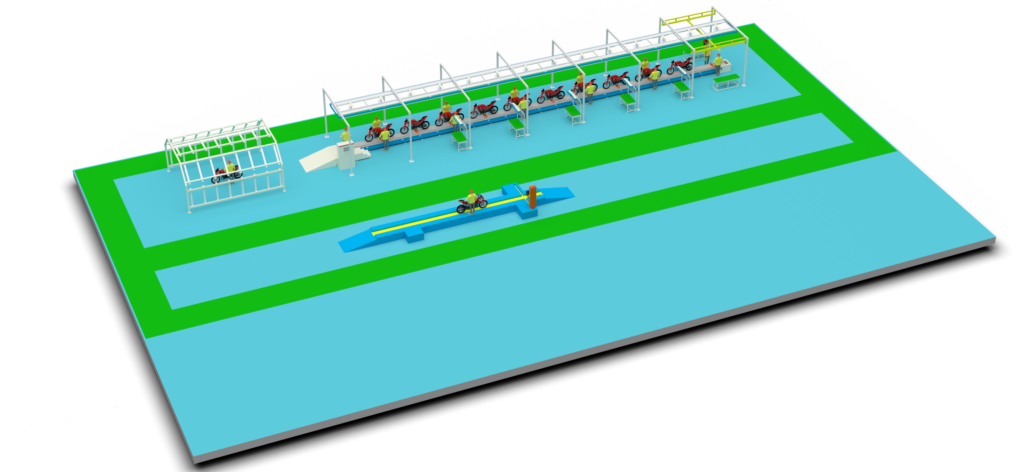
II. Overall Layout
E-bike production lines typically adopt a combination of modular island layout and linear assembly line:
1. Main Production Areas
- Frame Processing Zone: Metal material cutting, bending, and welding (automation rate ≥70%)
- Coating Zone: Electrophoresis, powder coating, and drying (independent enclosed workshop)
- Final Assembly Zone: Drive system, vehicle body, and electrical assembly
- Inspection Zone: Vehicle performance testing and safety compliance inspection
- Packaging & Logistics Zone: Finished product offline, warehousing, and shipping
2. Conveyor System
Utilizes plate-chain conveyor systems combined with AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) intelligent carts to achieve precise workpiece flow between different stations. Frame assembly adopts accumulated suspension conveyor lines, while final assembly lines typically use floor drag chains or plate-type conveyors.

III. Core Process Flow
(A) Frame Manufacturing & Coating
- Raw Material Preparation: Iron and aluminum material cutting and pre-treatment
- Welding & Forming: Options include fully automated welding robots for main frame welding or semi-automatic manual welding for complex frame structures
- Surface Treatment: Electrophoretic anti-rust treatment → Powder coating curing (using automated spraying and drying production lines)
- Precision Machining: CNC processing of mounting holes to ensure subsequent assembly accuracy
(B) Electrical System Pre-assembly
- Battery Module Assembly: Module stacking, BMS (Battery Management System) installation
- Wire Harness Pre-fabrication: Wire cutting, terminal crimping, continuity testing
- Motor & Controller Pairing: Magnetic powder dynamometer testing for motor performance, completion of controller programming
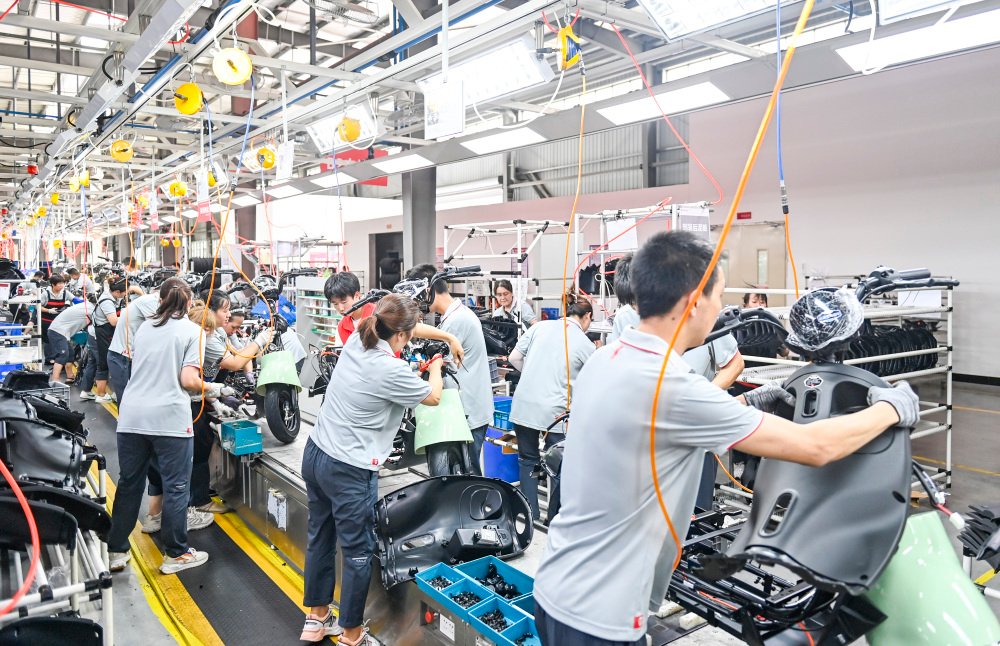
(C) Vehicle Assembly Process
The final assembly line typically consists of 15-20 workstations, adopting a human-machine collaborative operation mode:
| Workstation Stage | Core Operations | Key Equipment/Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Chassis Assembly | Motor installation, rear swing arm assembly, shock absorber installation | Torque-controlled screwdrivers (precise torque control) |
| Power System | Battery pack installation, controller fixing, main cable connection | Automatic screwdrivers, pneumatic wrenches |
| Front Assembly | Front fork, handlebar, instrument panel, brake system assembly | Automatic riveting guns |
| Wheel Assembly | Hub, tire, brake disc assembly and dynamic balancing test | Automatic tire mounting machines |
| Body Covering | Plastic parts installation, seat, footrest, protective panel assembly | Electric tightening tools |
| Wiring Routing | Vehicle circuit connection, lighting, signal system interfacing | Intelligent continuity testers |
(D) Vehicle Inspection & Debugging
After final assembly, every vehicle must undergo 100% comprehensive inspection:
- Function Testing: Motor performance, controller response, lighting signals, instrument display
- Safety Compliance Testing: Insulation withstand voltage test (≥1000V), ground continuity, waterproof rating test
- Road Test: Chassis dynamometer simulated load operation, braking performance, maximum speed, climbing capability
- Appearance Inspection: Paint quality, assembly gaps, labeling completeness
IV. Automation & Intelligent Features
1. Key Process Automation
- Fully Automatic Screw Locking Machines: Precise screw hole identification through sensors, torque error controlled within ±3%, solving the consistency issues of manual screw locking
- Automated Welding Workstations: Equipped with welding robots, automatic handling systems, and post-weld inspection equipment
- Intelligent Logistics: AGV carts for automatic raw material delivery and finished product transfer
2. Digital Management (MES System)
- Real-time collection of production data (process parameters, equipment status, quality information)
- Process deviation analysis and optimization control based on digital twin models
- Establishment of product full lifecycle traceability system, achieving “one vehicle, one file”
3. Flexible Production Capability
The production line adopts modular design, allowing quick adjustment of fixtures to realize multi-variety, small-batch mixed production, adapting to market demands for personalized models.
V. Quality Control System
1. Inspection Equipment Configuration
- Chassis Dynamometer: Testing vehicle power performance
- Frame Vibration Testing Machine: Verifying frame fatigue strength
- Walk-in Environmental Test Chamber: High-low temperature, humidity cycling tests
- Charge-Discharge Tester: Battery cycle life and safety testing
2. Quality Management System
- Strict implementation of the “Three-Inspection System” (Self-inspection, Mutual inspection, Specialized inspection)
- SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) standardized operations for key processes
- Establishment of daily control, weekly inspection, and monthly scheduling quality work mechanisms
3. Tamper-Proof Design
Implementation of tamper-proof measures at both software and hardware levels to ensure key components such as batteries, controllers, and speed limiters cannot be illegally modified.
VI. Industry Development Trends
- Intelligent Upgrading: Introduction of AI visual inspection, collaborative robot assembly, moving towards “lights-out factory” direction
- Green Manufacturing: Promotion of water-based coatings, powder coating processes, construction of exhaust gas treatment systems to meet ecological and environmental protection requirements
- Lightweight Technology: Application of new materials such as aluminum alloy and carbon fiber to meet the weight restrictions of new national standards
- Digital Supply Chain: Achieving data interconnection with upstream component enterprises to improve supply chain response speed
Conclusion: Modern e-bike production lines are the product of deep integration of mechanical engineering, electrical automation, and information technology. Through automation equipment, digital management systems, and strict quality control systems, they achieve efficient, precise, and stable large-scale production, providing reliable manufacturing guarantees for green transportation.
Our company specializes in producing e-bike production lines and can adjust the entire line structure according to customer requirements. If you have related needs, please contact us:
Contact Information:
- Email: laserautomation@qq.com
- WhatsApp: +86 13736558515
- Website: Production System Engineering Solutions Suite
