Free flow chain conveyor for assembly line
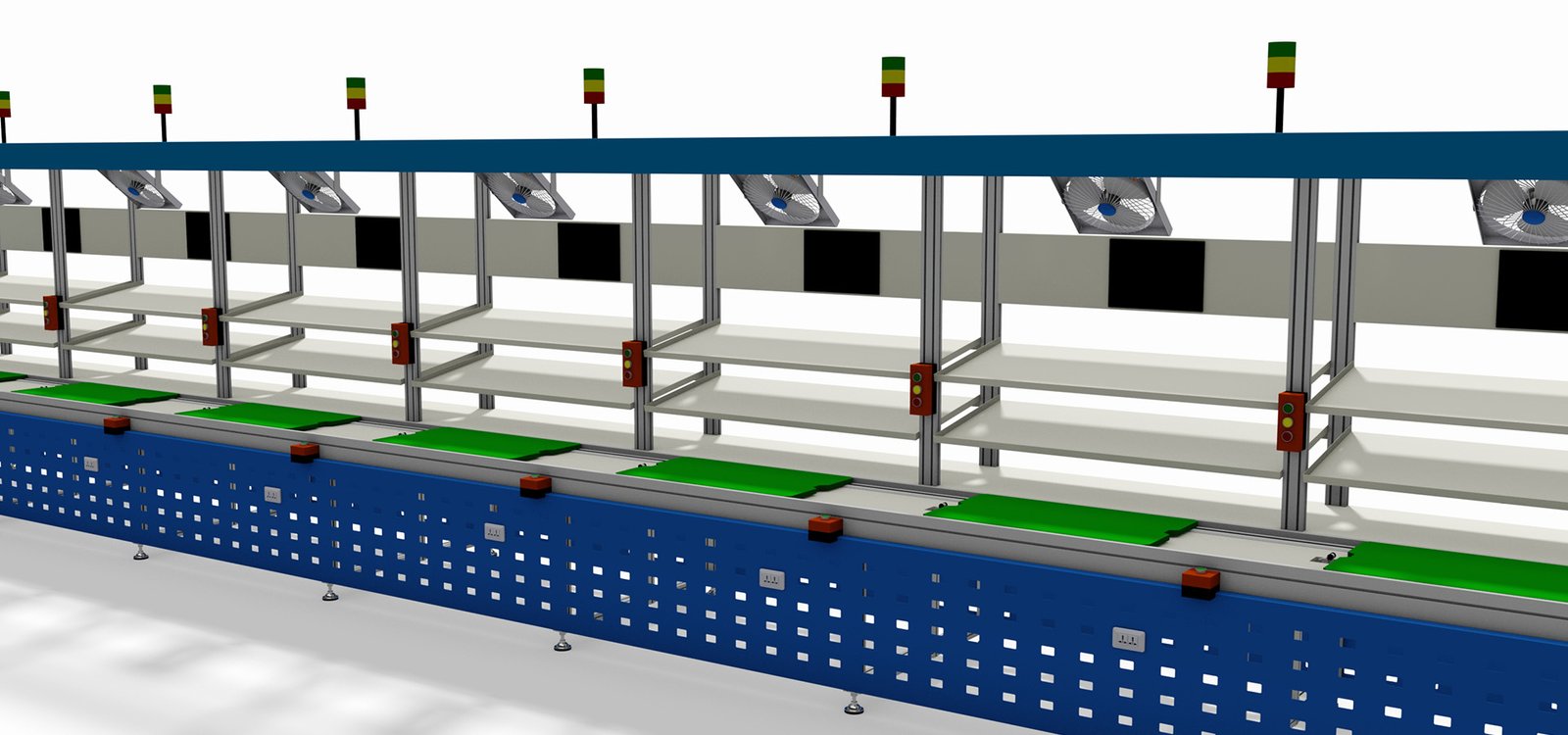
A Free Flow Chain Conveyor is an efficient conveying system specifically designed for assembly lines. It typically consists of a series of chains with freely rotating support rollers that can support and move workpieces or products placed on them. Here is a description of the Free Flow Chain Conveyor:
- Flexibility: The Free Flow Chain Conveyor can easily adapt to different production line layouts and product requirements because it allows for operations and assembly at any point along the conveyor.
- Continuous Flow: This conveyor supports continuous product flow without the need for stops or waiting, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of the production line.
- Modular Design: The Free Flow Chain Conveyor usually features a modular design, making it easy to install, adjust, and maintain.
- Ease of Integration: It can be integrated with other automated equipment and systems (such as robots, automated inspection stations) to achieve a higher level of automated production.
- Adjustable Speed: The speed of the conveyor can be adjusted according to production needs to accommodate different production paces.
- Low Maintenance: Due to its simple and durable design, the maintenance cost of the Free Flow Chain Conveyor is relatively low.
- Versatility: Suitable for a variety of shapes and sizes of products, including those that require multiple operations during the assembly process.
- Ease of Operation: Operators can easily add, remove, or adjust the position of products on the conveyor.
- Safety: The conveyor is designed to meet industrial safety standards, ensuring the safety of operating personnel.
- Cost-Effective: Although the initial investment may be higher, in the long run, the Free Flow Chain Conveyor can improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs, thus increasing the return on investment.
The Free Flow Chain Conveyor is an important tool for improving production efficiency and flexibility in modern manufacturing, especially suitable for assembly line environments that require high flexibility and quick response.
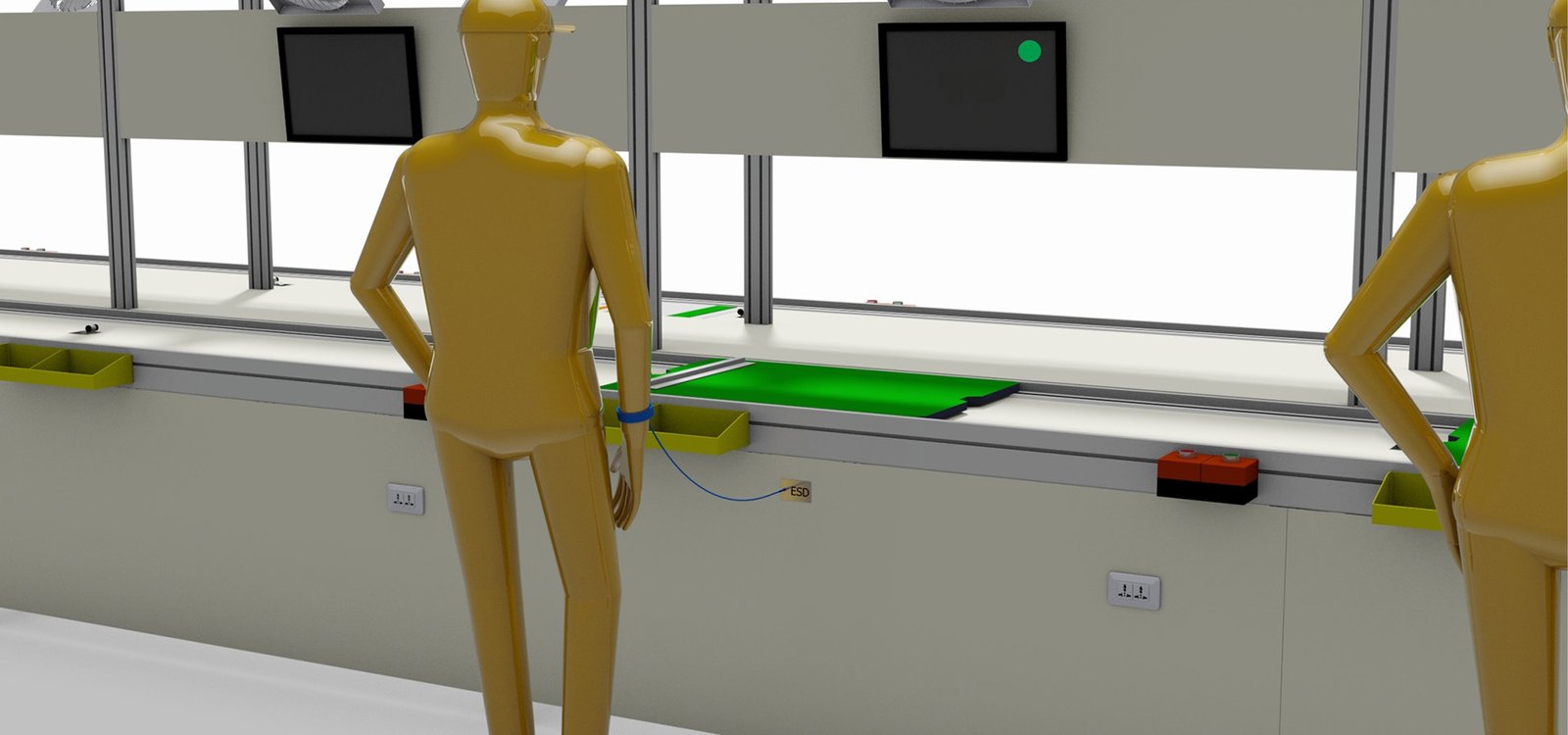

The integration of auxiliary equipment and systems in assembly lines can significantly improve production efficiency, product quality, and operational safety. Here are some common auxiliary supports:
- Automated Workstations:
- Used for performing specific assembly tasks, such as welding, riveting, gluing, or screw fastening.
- Material Handling Systems:
- Including Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), conveyors, lifts, etc., for moving materials along the production line.
- Quality Inspection Equipment:
- Such as vision inspection systems, dimensional inspection instruments, functional testing stations, etc., to ensure product quality.
- Robots:
- Used for tasks that are highly repetitive and require high precision, reducing manual operations.
- Tools and Fixtures:
- Used to secure and position workpieces for accurate assembly.
- Lighting Systems:
- Provide adequate lighting to ensure that operators can clearly see their work.
- Anti-Static Equipment:
- Such as anti-static floors, anti-static workstations, anti-static wristbands, etc., to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components from static electricity.
- Safety Protective Devices:
- Including emergency stop buttons, protective barriers, safety sensors, etc., to ensure the safety of operating personnel.
- Environmental Control Systems:
- Such as temperature and humidity control, air filtration systems, etc., to maintain a suitable production environment on the line.
- Data Acquisition and Monitoring Systems:
- Used for collecting data on the production line and monitoring the production process, achieving informatization of production management.
- Energy Management Systems:
- Used to monitor and optimize energy usage, reducing energy consumption.
- Material Storage and Supply Systems:
- Such as automated warehouses, material racks, automated feeding systems, etc., to ensure timely supply of materials.
- Cleaning and Maintenance Equipment:
- Used for cleaning and regular maintenance of the production line, keeping equipment in good operating condition.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI):
- Provide user-friendly operation interfaces, making it easy for operators to monitor and control the production line.
- Software Systems:
- Such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), etc., for production planning, scheduling, and tracking.
Integrating these auxiliary supports can increase the level of automation on the production line, reduce manual intervention, enhance production efficiency and product quality, while reducing production costs and improving operational safety.
