Options for Inline Laser Marking Equipment for Wood Products
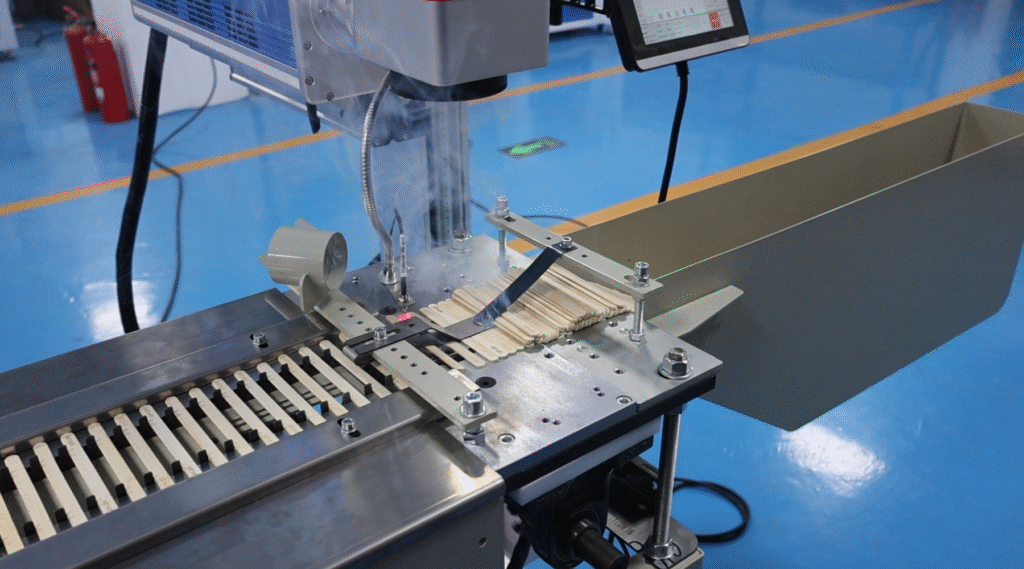
A Comprehensive Overview of In-line Laser Marking Machines for Wood Products
I. Features
(1) Non-contact Processing
- Principle: Laser marking works by focusing a high-energy laser beam onto the surface of wood products, causing the material to vaporize instantaneously or change color, thereby forming patterns or text. Throughout the entire processing procedure, there is no physical contact between the laser beam and the wood, avoiding the wear and deformation that may be caused by traditional mechanical processing methods.
- Advantage: This non-contact processing method is particularly suitable for wood products because wood is a relatively soft and easily damaged material. For instance, when marking on delicate wood carvings, laser marking will not destroy the original texture and shape of the wood carving, preserving its artistic value.
(2) High Precision and High Resolution
- Precision: Laser marking machines can achieve extremely high processing precision, mainly due to their advanced optical systems and high-precision motion control systems. The laser beam can be focused to a very small spot diameter, generally between 0.01 and 0.1 millimeters, or even smaller. This means that extremely fine patterns and text can be etched onto the wood surface.
- Resolution Advantage: High resolution ensures that the marked content is clear and distinguishable. Even small fonts or complex patterns can be precisely presented. For example, when marking brand logos on small wooden toys, high resolution ensures that every detail of the logo is clearly displayed, enhancing the product’s appearance quality.
(3) Wide Range of Applicable Materials
- Soft Wood: Soft wood is relatively soft in texture, and laser marking can easily etch various patterns and text on its surface without affecting the flexibility of the soft wood. For example, marking on cork wine bottle stoppers can include the winery name, production date, and other information.
- Hard Wood: For hard woods, such as oak and walnut, laser marking is equally applicable. Although hard woods have higher density and hardness, laser energy can penetrate the wood surface to form clear marks. In high-end furniture manufacturing, laser marking on the surface of hard wood can be used for product traceability and brand identification.
- Composite Wood Panels: Including plywood, particleboard, and other composite wood panels, laser marking can also be performed on these materials without causing damage to the internal structure. For example, marking product specifications and production batches on composite wood panels used for architectural decoration.
(4) Fast Marking Speed
- High-Speed Movement: The laser beam in a laser marking machine can move at high speeds under computer control, with speeds reaching 5 to 7 meters per second. This means that more marking tasks can be completed in a unit of time, significantly improving production efficiency.
- Software Control Advantage: Through professional marking software, marking patterns or text can be quickly designed and edited. Once the design is complete, the device can quickly etch this information onto the wood surface. For example, on the production line of a wood processing enterprise, the laser marking machine can quickly complete the marking as the wood panels pass through, enabling continuous production.
(5) Good Marking Effect
- High Contrast: Laser marking forms marks with high contrast on the wood surface because the laser energy can cause color changes on the wood surface (such as carbonization to black or ablation to form depressions), thereby creating a clear visual difference from the surrounding wood surface.
- Permanence: The marks are physically etched onto the wood surface and are permanent. Even after long-term use and exposure to environmental factors such as wind, sun, and rain, the marks will not easily fade. For example, on outdoor wooden furniture, the marks can remain clear for a long time, facilitating product identification and traceability.
II. Advantages
(1) Permanence and Durability
- Long-Term Stability: Marks formed by laser marking have strong durability and will not wear away due to daily friction, cleaning, and other operations. For example, anti-slip marks on wooden floors, even after frequent stepping and cleaning, can remain clear and provide long-term safety warnings to users.
- Environmental Adaptability: Marks can withstand a variety of harsh environments, such as humid and high-temperature environments. In some wood processing workshops where the humidity may be high, laser-marked marks can still remain stable and not become blurred due to moisture.
(2) Anti-counterfeiting
- Uniqueness: Laser marking technology can produce unique marking effects that are difficult to replicate. For example, by setting special laser parameters and designing complex patterns, unique marks with micro-texture features can be generated on the surface of wood products. These features can be observed with a high-power magnifying glass but are difficult to forge with ordinary printing or carving methods.
- Security: In high-end wood products, such as valuable wood handicrafts and limited-edition wooden collectibles, laser marking can serve as an anti-counterfeiting measure to protect the intellectual property rights of the products and the interests of consumers.
(3) Low Operating Costs
- Low Energy Consumption: Laser marking machines consume relatively little energy during operation. Compared with traditional mechanical engraving equipment, laser marking machines do not require complex mechanical transmission devices. Their main energy consumption comes from the laser and control systems, and they can be quickly turned off after marking is completed, saving energy.
- Low Maintenance Costs: The structure of the laser marking machine is relatively simple, mainly consisting of a laser, optical system, and control system, with no complex mechanical parts. Therefore, the failure rate is low. At the same time, the laser marking machine has few consumable parts. For example, the laser has a long service life (generally tens of thousands of hours), and optical lenses and other parts can maintain stable performance for a long time under normal use and maintenance, reducing maintenance costs.
- Few Consumables: During the marking process, no consumables are needed other than the wood itself. Compared with traditional marking methods such as inkjet printing or screen printing, laser marking does not require ink, ink, or screens, further reducing operating costs.
(4) Flexibility and Customization
- Free Pattern Design: Through professional marking software, users can freely design various patterns and text, including complex graphics, trademarks, QR codes, etc. These designs can be easily imported into the laser marking machine for quick marking.
- Personalized Customization: It can meet the personalized marking needs of different customers for wood products. For example, for custom furniture, unique marks or patterns can be applied to the surface of the furniture according to customer requirements, increasing the added value of the product and customer satisfaction.
(5) Environmental Protection and Pollution-Free
- No Chemical Pollution: The laser marking process does not use any chemical reagents, such as acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances, and does not produce chemical pollution. This is very important for wood processing enterprises because wood is a natural material, and environmentally friendly and pollution-free processing methods are more in line with the requirements of sustainable development.
- No Dust Pollution: Compared with traditional mechanical engraving methods, laser marking does not produce a large amount of dust. Although a small amount of smoke is generated during laser marking due to the combustion of wood, this smoke can be treated with a professional smoke exhaust system and will not cause environmental pollution or harm to the health of operators.
III. Considerations for Application
(1) Equipment Selection
- Laser Power: Choose the appropriate laser power according to the type of wood and marking requirements. For harder woods or deeper marks, a higher-power laser may be needed. For example, for hard wood carving, the laser power may be between 50 and 100 watts; for soft wood marking, a power of 20 to 50 watts may be sufficient.
- Marking Range: Consider the size and shape of the wood products and select equipment with an appropriate marking range. If the wood products are large, such as large wooden furniture panels, equipment with a larger marking range is needed; for small wood products, such as wooden ornaments, equipment with a smaller marking range but higher precision can be chosen.
- Control System Precision: A high-precision control system can ensure the precision and repeatability of the marking. When selecting equipment, pay attention to the brand and performance parameters of the control system, such as positioning accuracy and repeat positioning accuracy. For applications requiring high-precision marking, such as precision wooden instrument casings, the precision of the control system is particularly important.
(2) Operator Training
- Professional Training Courses: Operators should attend professional laser marking machine operation training courses. These courses usually include the basic principles of the equipment, an introduction to the operating interface, safety operating procedures, common troubleshooting, and other content. Through training, operators can master the operation methods of the equipment proficiently and improve work efficiency.
- Safety Awareness Cultivation: Laser marking machines emit laser radiation during operation, and operators need to have a strong sense of safety. The training should focus on laser safety protection knowledge, such as wearing protective goggles, avoiding direct exposure to the laser beam, and observing safe operating distances, to prevent laser damage to the eyes and skin.
- Software Operation Skills: Operators also need to master the operation skills of marking software, including pattern design, file format conversion, parameter settings, etc. Proficient software operation can ensure the accuracy and aesthetics of the marking patterns and reduce marking errors caused by operational mistakes.
(3) Environmental Requirements
- Clean Environment: The equipment should be placed in a clean environment to prevent dust and impurities from entering the interior of the equipment. Dust can adhere to optical lenses, affecting the focusing effect of the laser and reducing marking quality. Regularly clean the surrounding environment of the equipment and keep the surface of the equipment clean and tidy.
- Dry Environment: Humidity also affects the performance of laser marking machines. High humidity can cause electronic components inside the equipment to become damp, affecting their normal operation. Generally, the equipment should be placed in an environment with a relative humidity of less than 70%, and dehumidifiers can be equipped if necessary.
- Good Ventilation: The laser marking process generates smoke and heat, and a well-ventilated environment can promptly exhaust this smoke and heat to ensure the normal operation of the equipment. Install ventilation ducts or exhaust fans near the equipment to ensure good air circulation.
(4) Maintenance and Care
- Optical Lens Cleaning: Optical lenses are key components of laser marking machines, and their cleanliness directly affects the focusing effect of the laser. Regularly clean the lenses with dedicated optical lens cleaning agents and dust-free cloths. Avoid using cleaning agents containing alcohol or other corrosive components to prevent damage to the lens surface.
- Laser Source Inspection: Regularly check the working condition of the laser source, including laser output power, laser beam quality, and other parameters. If a decrease in laser power or deterioration of laser beam quality is detected, the laser source should be repaired or replaced in time. The service life of a laser source is generally tens of thousands of hours, but it should also be checked according to actual usage.
- Lubrication of Moving Parts: For moving parts in the equipment, such as worktables and galvanometers, regular lubrication should be performed. Use dedicated lubricating oil or grease and lubricate according to the instructions in the equipment manual to reduce wear on moving parts and extend the service life of the equipment.
- Smoke Exhaust System Maintenance: The smoke generated during the laser marking process needs to be exhausted through the smoke exhaust system. Regularly check the smoke exhaust system’s ducts for blockages and whether the filter needs to be replaced to ensure good smoke exhaust effects. If the smoke exhaust system has problems, it may lead to smoke accumulation around the equipment, affecting the health of operators and the performance of the equipment.
(5) Safety Protection
- Protective Goggles: Operators must wear protective goggles when operating laser marking machines. Protective goggles can effectively block laser radiation and protect the eyes from damage. Choose protective goggles according to the laser’s wavelength and power to ensure their protective effect meets safety standards.
- Safety Light Curtains and Protective Covers: Install safety light curtains and protective covers around the equipment to prevent laser beam leakage. Safety light curtains can immediately cut off the laser output when detecting the human body entering the danger zone, and protective covers can confine the laser beam within the equipment to prevent laser harm to surrounding personnel.
- Emergency Stop Button: The equipment should be equipped with an emergency stop button, which operators can quickly press to stop the equipment in case of emergency. The emergency stop button should be placed in a position easily accessible to the operator to ensure a quick response in an emergency.
- Safety Signage: Post clear safety signs around the equipment to remind operators and surrounding personnel of laser safety. Safety signs should include information about the laser’s category, power, danger zone, etc., to make people aware of the equipment’s dangers and safety precautions.
