Electric Scooter Assembly lines Plant Two-wheeled electric vehicles
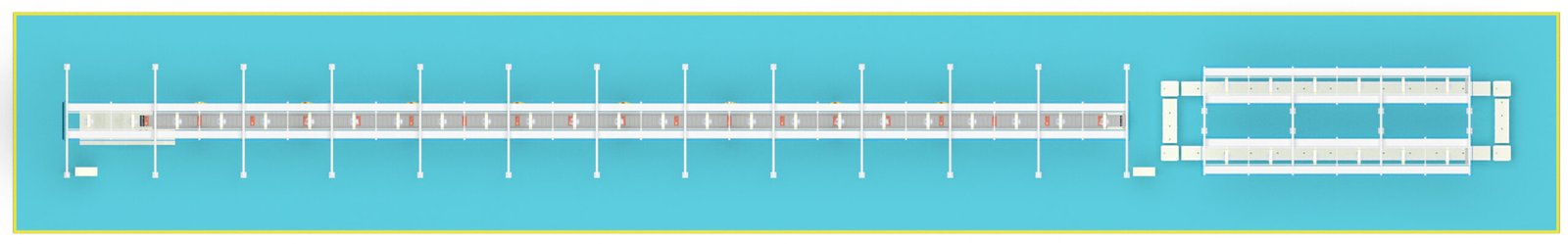
Two-wheeled electric vehicle assembly lines are pivotal to the production process, ensuring efficiency, quality, and consistency in manufacturing. They automate and streamline various stages, from component preparation to final testing, reducing manual labor and the potential for human error. This automation enhances productivity, allowing for a higher output of vehicles in a shorter time frame. Additionally, integrated quality control systems within the assembly line help maintain stringent standards, ensuring each vehicle meets performance and safety requirements. The use of advanced technologies such as robotics also facilitates better traceability and oversight, which is crucial for timely identification and resolution of production issues, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
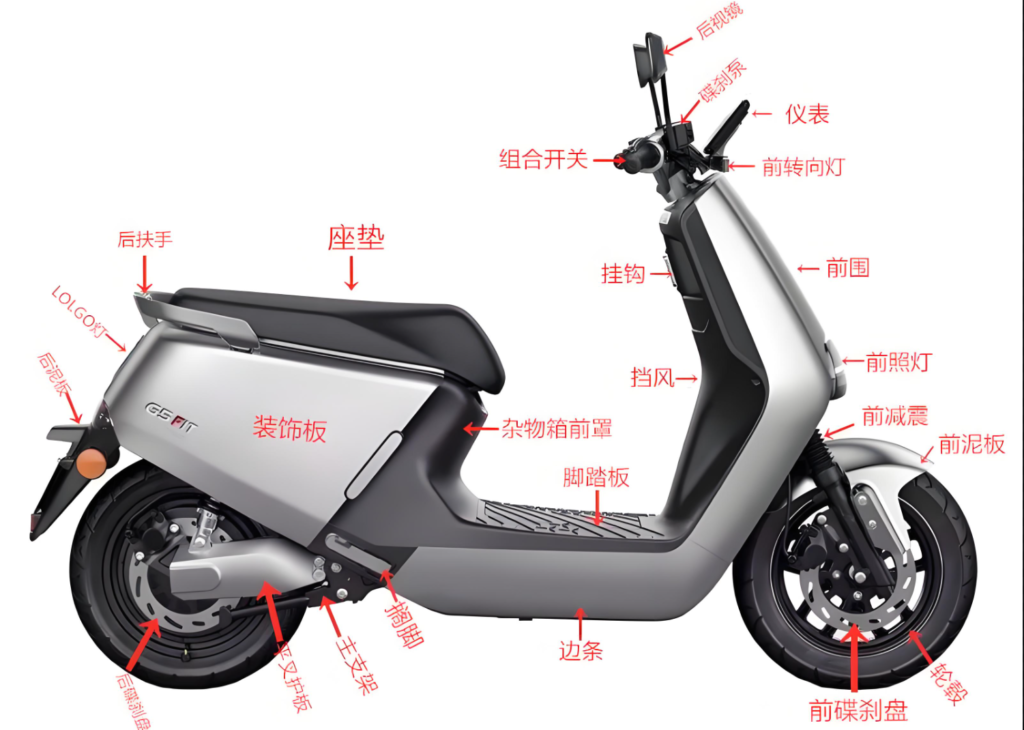

Two-wheeled electric vehicles are primarily composed of the following components:
- Frame: Serves as the fundamental structure of the electric vehicle, supporting the entire vehicle.
- Battery: Provides electrical energy and is the power source of the electric vehicle.
- Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle.
- Controller: Regulates the operation of the motor and manages the charging and discharging of the battery.
- Electrical System: Includes lighting, signal lights, instruments, and other electrical equipment.
- Body and Fairings: Provide protection for the rider and aesthetically enhance the vehicle’s appearance.
- Suspension System: Connects the wheels to the frame, offering cushioning and stability.
- Braking System: Controls the vehicle’s deceleration or stopping.
- Tires and Wheels: Support the vehicle’s weight, make contact with the ground, and provide the traction necessary for movement.
- Steering System: Allows the rider to control the direction of the vehicle.
- Seat: Offers a comfortable riding experience for the driver and passenger.
- Instrument Panel: Displays information such as speed, battery level, and mileage.
- Charger: Used for charging the battery.
- Cables and Connectors: Link the various electrical components of the electric vehicle.
- Accessories: Such as luggage racks, windshields, anti-theft devices, etc., which vary according to the model and user requirements.
These components work together to form the basic structure of a two-wheeled electric vehicle, enabling it to operate safely and efficiently. Different models and brands of electric vehicles may vary in the specifications and technology of their components.

The assembly production process of two-wheeled electric vehicles typically includes the following key steps:
- Component Preparation: Begin by preparing the core components such as the frame, battery, motor, and controller, as well as other parts like lights, dashboard, tires, etc.
- Frame Assembly: Install the electric motor, battery, and other core components onto the frame, ensuring their correct positioning and stability.
- Battery and Motor Installation: Assemble the battery into the vehicle’s battery compartment and connect it to the motor, completing the electrical circuit connections.
- Electrical Control System Installation: Install the controller and connect the wiring harness, ensuring that all electrical connections are correct to guarantee the normal operation of the vehicle’s electronic control system.
- Body Assembly: Install external parts such as body panels, lights, and dashboard to complete the vehicle’s exterior assembly.
- Suspension and Braking System Installation: Complete the assembly of the suspension and braking systems to ensure driving stability and safety.
- Performance Testing: Conduct performance tests on the assembled electric vehicle, including motor performance, battery life, and braking effects, to ensure that all vehicle performance indicators meet standards.
- Quality Inspection: Perform a final quality inspection of the electric vehicle, including appearance checks and functional tests, to ensure that all parts meet standards and are qualified.
Automated assembly lines play a crucial role in improving production efficiency and product quality. They typically include an automatic conveying system, robotic welding, modular assembly lines, automated testing equipment, and information management systems to achieve automation and informatization of the production process.
The entire production process, from the storage of raw materials, component quality inspection, component assembly, frame and electrical component assembly, electrical performance testing, exterior assembly and testing, to the final road testing, inspection, serial number entry, finished product quality inspection, sorting and packaging, and shipping, all require strict operation and quality control to ensure that each electric vehicle meets quality standards before leaving the factory.
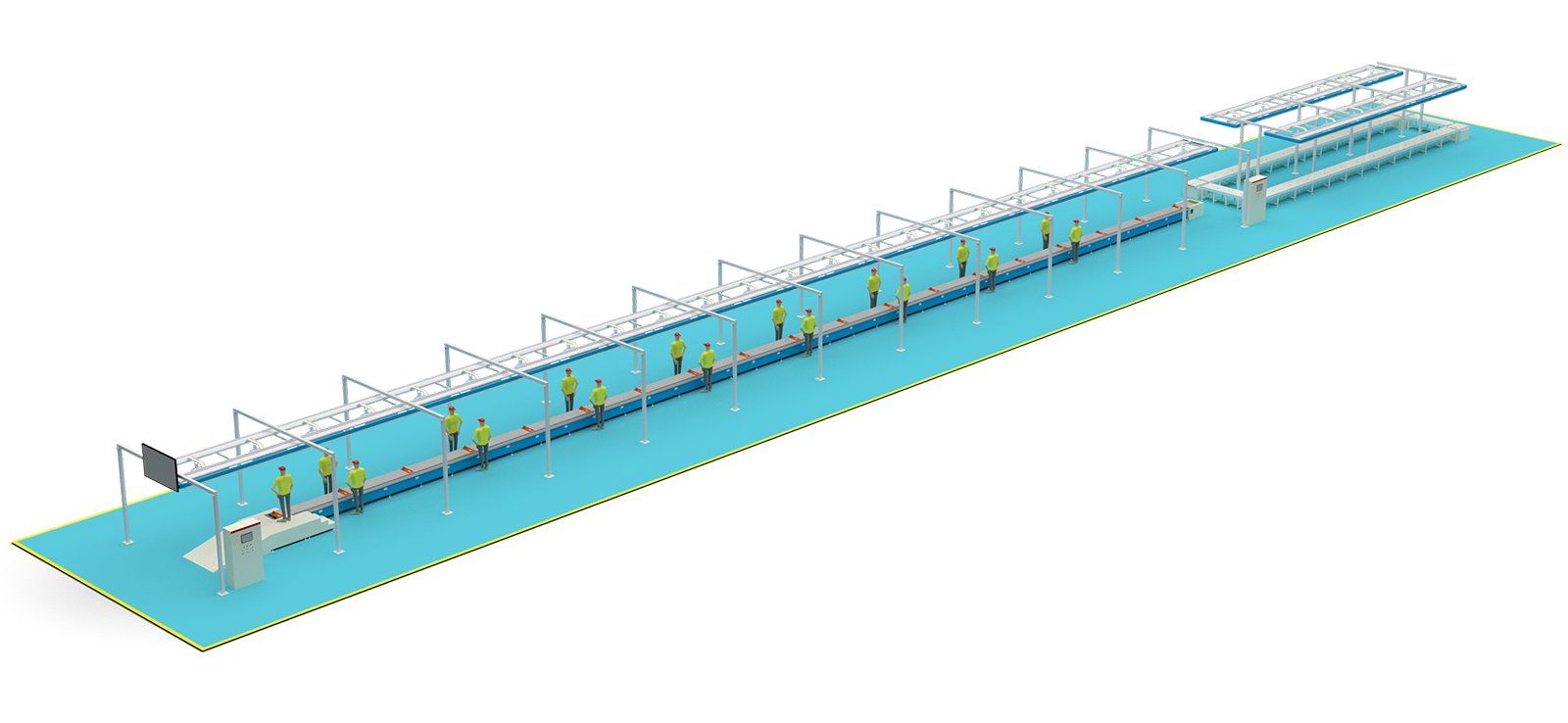
Pre-assembly production line equipment for wiring harness and tire installation of two-wheeled electric vehicles.
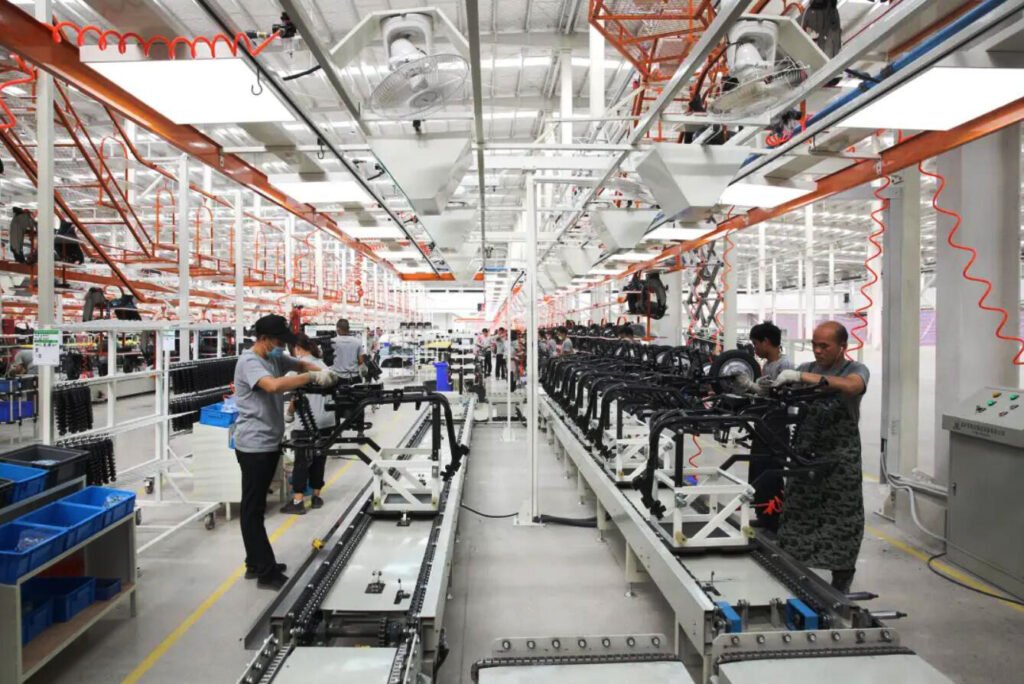

Electric Scooter Final Assembly line Plant
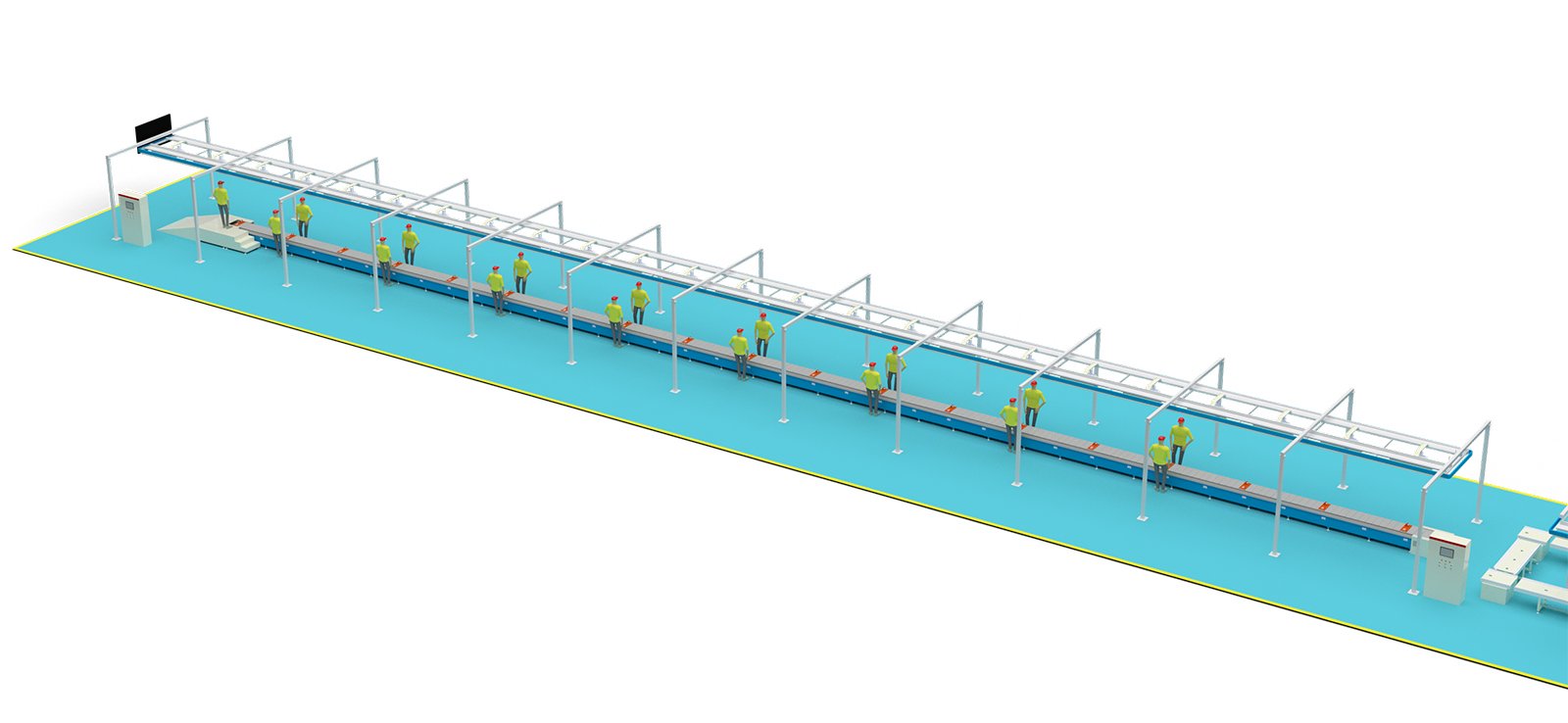
The daily output of a two-wheeled electric vehicle production line is influenced by a variety of factors, including the degree of automation of the production line, the proficiency of workers, and the stability of equipment operation. Generally speaking, a highly automated production line can complete more production tasks in a shorter period of time.
Without specific brand information, we can refer to the general level within the industry. A highly efficient two-wheeled electric vehicle production line, if it can produce a vehicle every 36 seconds, could theoretically produce about 100 units per hour (60 seconds / 36 seconds). If it operates 8 hours a day, the daily output would be approximately 800 units. This is a simplified estimate, and actual production capacity may increase due to production line optimization, overtime work, multi-shift production, and other factors.
Moreover, some modern electric vehicle production lines also adopt information management systems, such as MES systems, which help to improve production efficiency and product quality, further increasing daily output. However, the specific number for daily output still needs to be determined based on actual production conditions.
