Handheld laser welder for production line applications
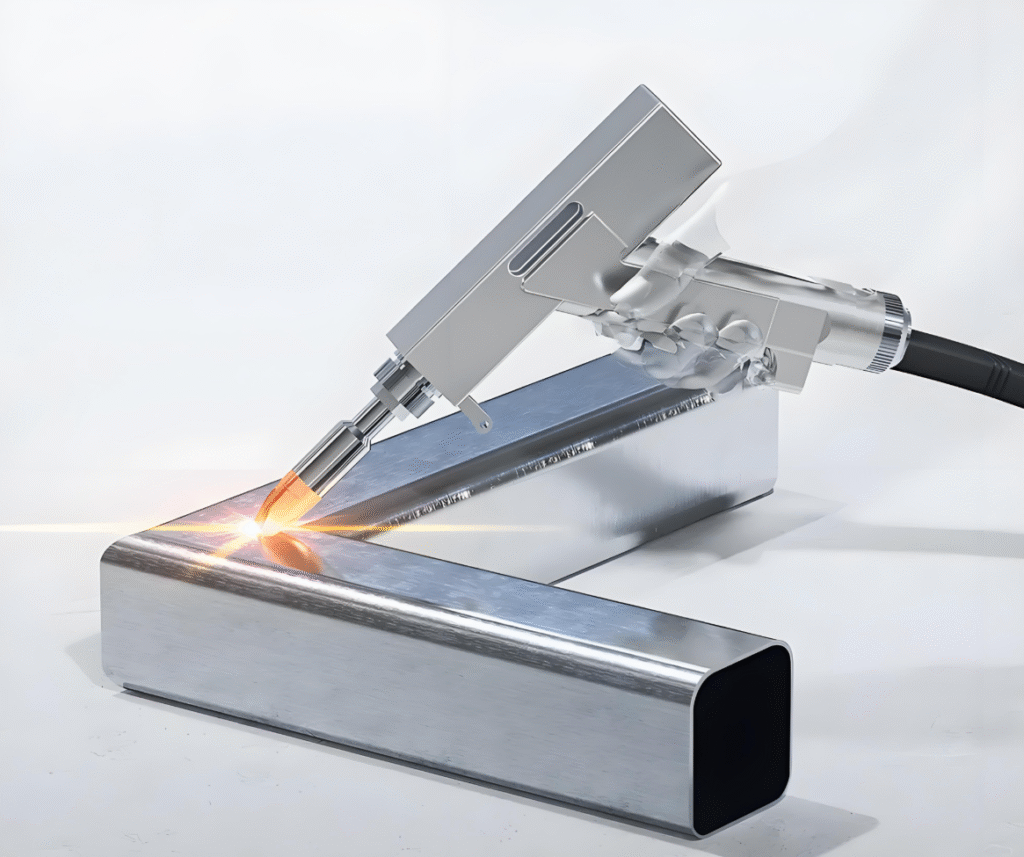
Handheld laser welding machines have the following main characteristics, application scenarios, laser types and power output methods, as well as material suitability:
Characteristics:
- High Efficiency and Speed: Fast welding speed, capable of completing the welding process within seconds, significantly improving production efficiency and reducing material oxidation.
- Simple Operation: Easy to learn and use, no professional welding knowledge required, operators can become proficient after simple training.
- Excellent Welding Quality: Smooth and aesthetically pleasing weld seams without fish-scale patterns, no need for post-weld grinding, small heat-affected zone, and minimal welding deformation.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Handheld operation, portable, suitable for outdoor and long-distance welding, with a wide range of accessibility.
- No Consumables: No need for filler wire or other consumables during the welding process, reducing production costs.
- Environmentally Friendly and Energy-saving: High electro-optical conversion efficiency of the laser (up to 30%), low energy consumption, minimal smoke and harmful gases produced during welding.
- Multi-functional: Supports various welding methods such as vertical welding, butt welding, fillet welding, and overlap welding, adapting to diverse welding needs.
Application Scenarios:
- Sheet Metal Processing: Welding of metal sheets such as stainless steel and aluminum alloys.
- Kitchenware Manufacturing: Welding of stainless steel pots, pans, and other kitchen utensils.
- Advertising Industry: Welding of metal products like billboards and signage.
- Fitness Equipment: Welding of metal components in fitness equipment.
- Medical Devices: Welding of precision medical devices requiring high accuracy and low deformation.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Welding of automotive components such as body parts and engine components.
- Aerospace: Welding of aerospace components requiring high strength and lightweight.
- Electronics and Communication: Welding of electronic device casings and heat sinks.
- Repair and Modification: Used for on-site repair and modification without the need to disassemble workpieces.
Laser Types and Power Output Methods:
- Laser Types:
- Fiber Lasers: Currently the mainstream, offering high electro-optical conversion efficiency, fast heat dissipation, maintenance-free operation, and long service life.
- Other Types: Such as xenon lasers, argon lasers, and tungsten-titanium lasers, but these are less commonly used in handheld devices.
- Power Output Methods:
- Continuous Output: Most handheld laser welding machines use continuous laser output, suitable for most welding tasks.
- Modulated Output: Some devices support modulated laser output for special welding requirements.
- Power Range:
- Common power ratings range from 0.5kW to 3kW, suitable for welding metal sheets up to 3mm thick.
- High-power devices (above 3kW) can be used for thicker materials or applications requiring deeper penetration.
Material Suitability:
- Metal Materials:
- Stainless Steel: Most common, with excellent welding results and aesthetically pleasing weld seams.
- Aluminum Alloys: Suitable for welding, but attention must be paid to high reflectivity issues.
- Copper Alloys: Weldable, but requires high power and special parameters.
- Titanium Alloys: Suitable for aerospace applications, offering high welding quality.
- Carbon Steel, Galvanized Sheets: Suitable for welding, widely used in the sheet metal industry.
- Non-metal Materials:
- Ceramics: Some devices can weld ceramics, but it is more challenging.
- Material Thickness:
- Generally suitable for welding thin sheets 3mm and below.
- With integrated wire feeding devices, metal sheets up to 4mm can be welded.
Summary:
Handheld laser welding machines are widely used in industries such as sheet metal, kitchenware, advertising, medical, automotive, and aerospace due to their advantages of high efficiency, flexibility, ease of operation, and excellent welding quality. Mainstream devices use fiber lasers with power ratings ranging from 0.5kW to 3kW, suitable for welding thin sheets of various metal materials such as stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper, and titanium, especially for sheets with 3mm and below thickness. Their characteristics of no consumables, low energy consumption, and environmental friendliness also make them increasingly popular in modern manufacturing.
