Reference Guide for Heat Pump Water Heater/Hot Water Boiler Assembly Line
A heat-pump water heater integrates compressor, evaporator, condenser and insulated tank. On the automated slat conveyor, robots fit these parts, charge refrigerant and inject foam, then tighten torque-controlled bolts. Subsequent stations vacuum-test, leak-check, measure heating capacity, COP, electrical safety and noise. Vision systems verify labels and welds. Finished units slide into corner-protected cartons, film-bagged, palletised and shrink-wrapped. MES tracks every serial number, schedules takt, stores test data and feeds ERP, giving full traceability and paperless quality control.
I. Structure of a Heat-Pump Water Heater
A heat-pump water heater is mainly composed of the following core parts:
- Heat-Pump System (refrigeration cycle):
- Compressor: compresses low-temperature, low-pressure refrigerant vapor into high-temperature, high-pressure gas.
- Condenser: releases heat to warm the water.
- Evaporator: absorbs heat from ambient air.
- Expansion Valve: reduces refrigerant temperature and pressure to complete the cycle.
- Water-Tank System:
- Inner tank: stores hot water, usually made of stainless steel or enamel-coated steel.
- Insulation layer: polyurethane foam to minimize heat loss.
- Outer shell: protects internal components and provides an aesthetic finish.
- Heat-exchange coil / condenser: transfers heat to the water inside the tank.
- Control System:
- Includes thermostats, sensors, main control board, etc., enabling automatic operation and protection functions.
- Auxiliary Components:
- Refrigerant piping, water pump, fan, filter drier, etc.
II. Assembly Process
Typical assembly steps are:
- Tank fabrication & hole punching: create openings for refrigerant pipes, water inlet/outlet, etc.
- Heat-exchanger installation: insert condenser or coil into the tank and seal to end-caps.
- Foam insulation: inject polyurethane foam between the inner tank and outer shell.
- Heat-pump unit mounting: install compressor, evaporator, expansion valve, and connect refrigerant lines.
- Electrical wiring: connect control board, sensors, power leads, etc.
- Sealing & leak check: perform airtight tests on the refrigerant circuit.
- Performance run-test: function, performance, and safety tests.
- Cosmetic finishing & packaging.
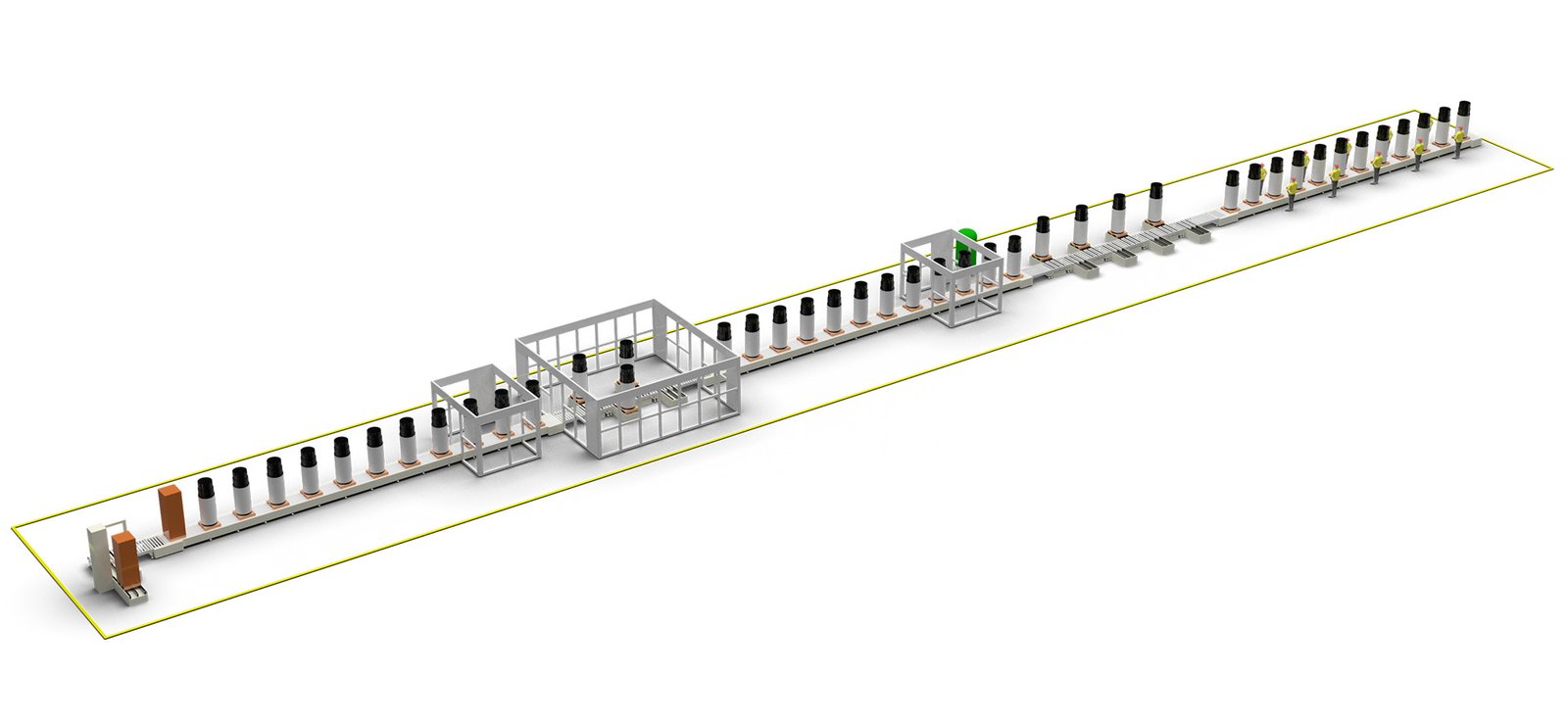
III. Assembly Line, Test Line, and Packaging Line
1. Assembly Line
- Conveyance: usually a combination of slat conveyor and roller conveyor, paced to takt time.
- Workstations: compressor mounting, refrigerant piping, electrical wiring, foam filling, etc.
- Automation equipment:
- Automatic nut-runners (torque-controlled)
- Industrial robots (handling, assembly)
- Vision systems (recognition, positioning, inspection)
- Automatic material feeding
- Jigs & fixtures (ensure accuracy)
2. Test Line
- Tests performed:
- Airtightness (helium mass-spectrometer leak test, pressure decay)
- Refrigerant charge weight check
- Performance (heating capacity, COP)
- Electrical safety (insulation, grounding, hi-pot)
- Vibration & noise
- Visual defects (scratches, dirt, labeling)
3. Packaging Line
- Packaging structure:
- Top pad, middle pad, bottom pad, corner protectors, pallet
- Bottom pad has fasteners that lock to the pallet for transport stability
- Process:
- Automatic bagging, case sealing, labeling
- Cushioning: foam, EPE, honeycomb board
- Optional automatic palletizing system
IV. MES (Manufacturing Execution System)
MES plays a key role in heat-pump water-heater production. Main functions:
- Production Planning & Scheduling:
- Adjust tasks in real time, optimize resource allocation
- Dynamically respond to order changes, reduce idle time
- Quality Management:
- Real-time collection of quality data, automatic pass/fail judgment
- Full traceability to quickly locate defective lots
- Links to test equipment to log results automatically
- Equipment Management:
- Real-time monitoring of machine status, predictive maintenance
- Fault alarms and repair-history tracking
- Increases uptime and utilization
- Traceability & Reporting:
- Every unit’s production history, materials used, and test data are traceable
- Automatic generation of production reports, quality analytics, efficiency KPIs
- Integration with Other Systems:
- Interfaces to ERP, PLM, WMS for end-to-end digital flow
- Supports barcode/RFID data capture to improve speed and accuracy
Summary
Manufacturing a heat-pump water heater is a complex process that combines thermodynamics, electrical control, and high-level automation. Modern plants integrate advanced assembly, testing, and packaging lines with a full-featured MES to achieve complete digital and intelligent management from raw material to finished goods. This not only boosts product quality and production efficiency but also provides a solid foundation for smart-manufacturing upgrades.
